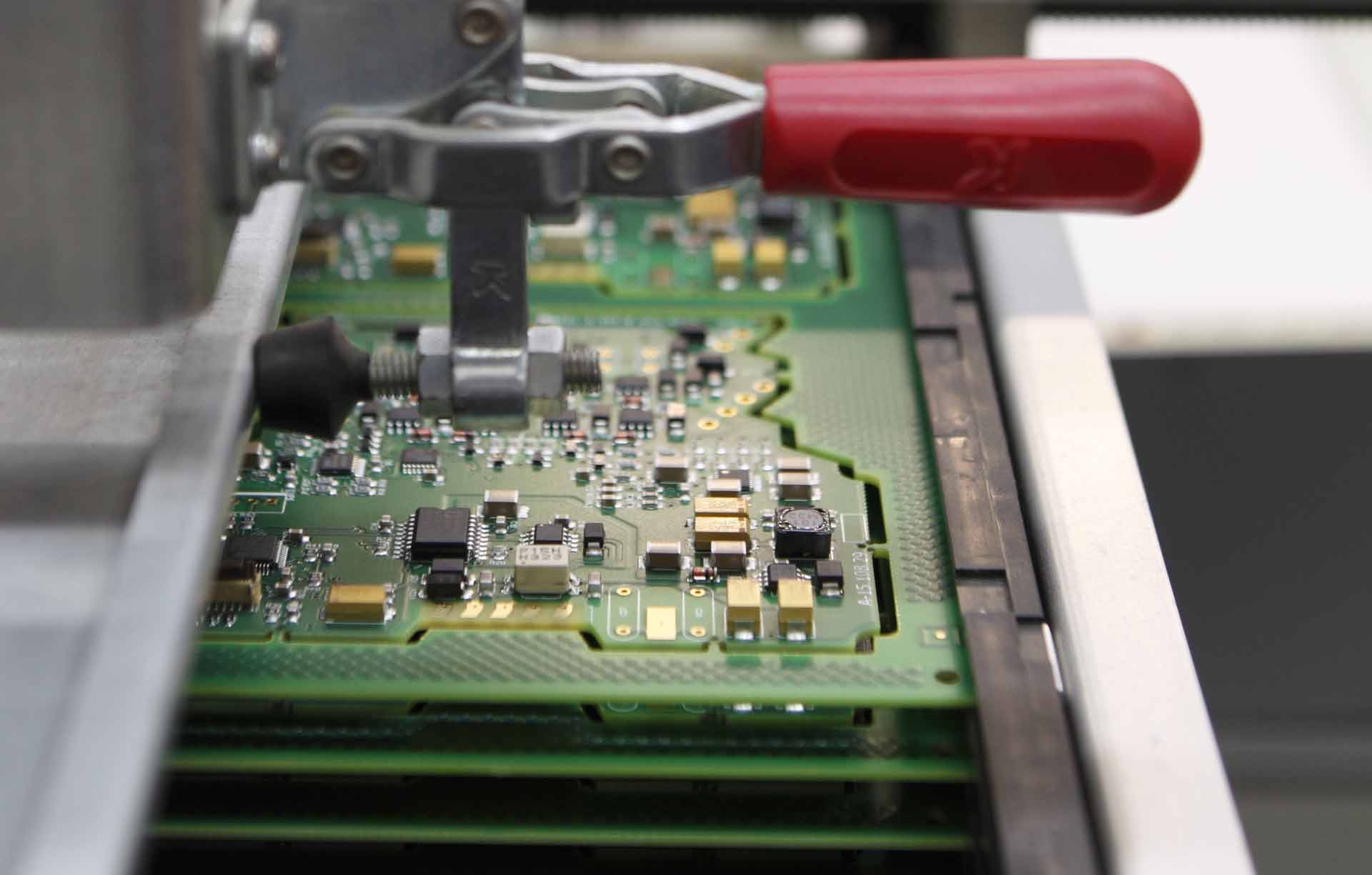
When the PCB assembly is completed, the module is sent for testing and verification. Together with the hardware, the consumer receives programs for the operation of the printed circuit board.
Normative base
The concept of a base module is used in the standardization system. This is a printed circuit assembly, supplemented with ERE, fasteners, and components for connection and fixation. The kit is designated EM1. Finished electronic devices are assembled from structurally finished assembly units.
The standard for mounting printed circuit boards is present. According to the document, the customer is responsible for choosing the quality class. The parameter is specified in the application.
Depending on the purpose of pcb design and development of electronic equipment, there are three groups:
Class A – general-purpose electronic devices: peripherals, PCs, modules and blocks that are part of standard complexes.
The difference between groups B and A is the obligatory fulfilment of the requirements for reliability and durability of work. The customer has the right to set strict requirements for operating conditions. Regardless of the turn-on time, the printed circuit assembly must work without failures. Products are installed in process control units. Application – medicine life support systems, transport, hazardous industries.
Class B: specialized equipment. The group includes communication devices, complex electronics and computer technology.
Class C: responsible devices.
After assembly, they control the failures in the operation of the unit and the quality of the soldering of parts in the printed circuit board. Full compliance with the requirements is desirable, but not required. The user and the contractor agree on tolerances.
The standard obliges the customer to inform about the nature of the effect of the external environment on the unit. The ideal option is that the printed circuit board works flawlessly in the event of adverse factors.